The age of alternative meats is upon us.
Beyond Meat is a $5 billion public company selling burgers in Canadian McDonald’s and American Carl’s Jr., breakfast sausages in Dunkin, and even chicken in a limited trial at KFC. Meanwhile, Impossible Foods has become a runaway hit at Burger Kings around the country. And the company is reportedly seeking to raise $300 million and $400 million at a valuation of roughly $3 billion according to reports in Reuters.
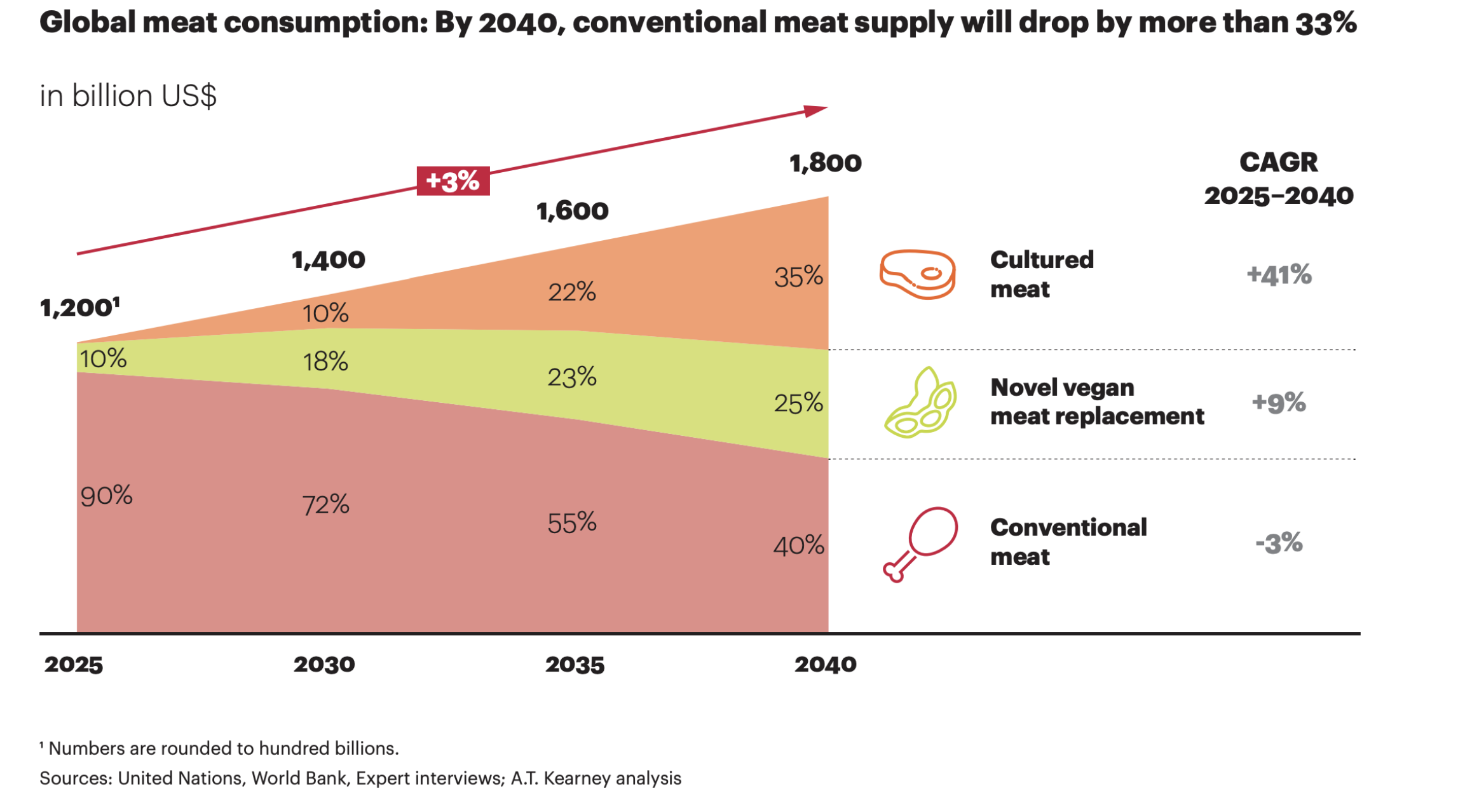
The plant-based up-and-comers have become a big enough threat that the meat industry has hired a marketing hit man to go after the new plant-based contenders to an increasing share of meat’s market. And they have a reason to be worried. By 2040, the conventional meat supply will drop by more than 33%, according to a report from the consulting firm AT Kearney.
As these no-longer-startups bask in the warm glow of success (and the rejuvenation of a sleepy corner of the supermarket) the question is what’s coming next from the research labs and test kitchens that are backed by millions in venture capital dollars.
Where’s the beef?
For the initial wave of investment, driven in part by a desire to appeal to consumers looking for alternatives to animal products, but wary of the cost of cultivating muscle tissue plant-based alternatives seemed obvious. Brown says animals are wholly unnecessary to make products that recreate the taste of a beef steak or a burger — and potentially surpass their flavor, all at a lower price.
Other companies have taken up that challenge as well in the months since Beyond Meat’s historic run in public markets (for a while, the company was the best-performing public offering of 2019). Startups like Rebellyous, Nuggs, and Daring Foods are making chicken replacements (along with big meat producer Tyson Foods through its Raised & Rooted brand).
Meanwhile beef gets its own challengers (outside of Impossible Foods and Beyond Meat) with companies like Nestle’s plant-based pitch Sweet Earth Foods, Tyson Foods, Beyond the Butcher, Hungry Planet and a host of others.
Even shrimp has a plant-based competitor in New Wave Foods, a startup that actually raised cash from Tyson’s venture capital arm earlier this year.
What has set Impossible Foods and Beyond Meat apart from other competitors — at least in the eyes of the investors — is the research and development teams that are working on flavor profiles and products that simply are more direct corollaries to the products they’re looking to supplant.
For Impossible, that’s the use of genetically modified yeast cells that are manufacturing a protein found in soy called leghemoglobin. That’s the core of Impossible’s secret weapon — the use of heme (a protein found in blood) to make its plant products taste meaty.
These same benefits apply to investors’ approach to plant-based dairy alternatives that are trying to one-up soy and almond milks with a more direct one-to-one substitute for dairy.