Global politics are difficult to navigate ordinarily, but in times of conflict companies that aim to provide an unbiased service, such as a map or search function, may have to come down on one side or another. Apple just came down at least partly on the side of Russia in its controversial annexation of Crimea from Ukraine, and Google has accommodated Russian interests as well.
The large peninsula on the north side of the Black Sea was brought under Russian control in 2014 during political unrest there concerning Crimea’s status within Ukraine. World leaders decried the move, saying that Russia had deliberately helped instigate the crisis there in order to take advantage of it, and violated Ukraine’s sovereignty with its military presence.
While the controversy surrounding these events are ongoing (indeed, the events themselves are too, in a way), companies like Apple and Google don’t have the luxury of waiting for history’s judgment to do things like update their maps.
Both, for instance, have in the past labeled locations in Crimea as being part of Ukraine. But Russia has made official complaints to the companies and warned them that it is considered a criminal act to refer to Crimea as other than a Russian territory. Now both companies have made concessions to Russian demands.
Apple in its Maps and Weather app now shows locations in Crimea as being part of Russia, when being viewed from that country. Russian authorities today said that “Apple fulfilled its obligations and brought the applications on its devices in compliance with the requirements of the Russian legislation.”
If you’re viewing from the U.S., both Apple and Google appear to take something of a neutral stance, if any stance can be said to be neutral. The Crimean peninsula appears as neither Russian nor Ukrainian on both Apple and Google Maps, with some rather strange gymnastics to accomplish it.
For example, in Google Maps there is a prominent border on the north side dividing Crimea from Kherson Oblast (a Ukrainian province), much heavier than lines between other provinces. Clicking Kherson Oblast on the border brings up a description and outline, while clicking Crimea seems to do nothing at all. On cities and random locations located in Crimea, there is no country at all in the space where it is normally displayed:
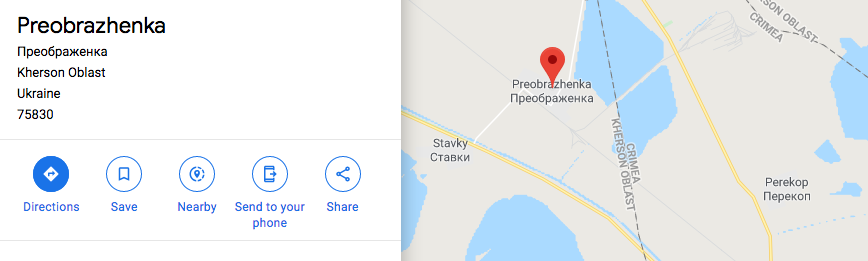
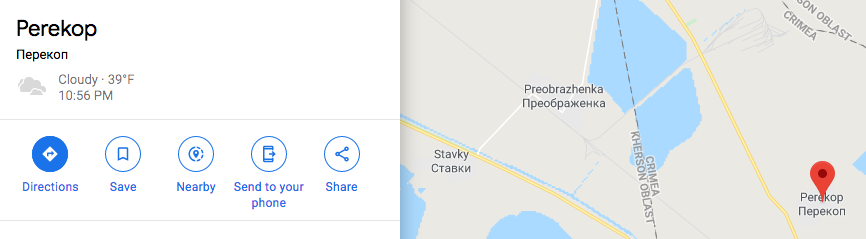
On both Apple and Google Maps, there is no border at all between Crimea and Russia where it would normally appear, across Taman Bay. Yet on one side of the bay locations are prominently labeled as Russian, while on the other they are devoid of a country affiliation.
I’ve asked Google and Apple for comment on when and how they decided to implement their current maps and will update this post if I hear back. It’s very likely that both will justify these decisions with the fact that they must adhere to local laws. But what happens when two sets of local laws diverge in the same location?
Update: A Google spokesperson says: “We make every effort to objectively depict the disputed regions, and where we have local versions of Google Maps, we follow local legislation when displaying names and borders.”
My point here is not to take sides for or against any of these representations, but to show that companies like Apple and Google are in a tight spot when it comes to these situations, and their information is far from complete or authoritative. In this case we see that they have different results for different places, concessions for some governments in spite of international concern, and the reduction of some services to a non-functional state (comparatively) in order to avoid controversy.
Just something to keep in mind whenever you look up information on services provided by global companies — they’re not objective sources, though of course arguably nothing is.



